High-Performance Vision Guidance
VSTeach
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive collects samples of image feature data or object poses from the visual system multiple times and outputs their average values.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to record the features of the target image or the poses of the target object after moving the robot to the target position. You can record the values of the output parameters of this primitive into variables and then use them in the primitives [HPImageBasedVS] or [HPPoseBasedVS].
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
objName* |
Object name used by visual servoing |
OBJNAME |
none |
|
objIndex |
Object index used by visual servoing |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 1] |
collectTimes |
Number of times of collecting image feature samples |
INT |
none |
30 ∈ [10 … 200] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
teachFinished |
Flag to indicate whether the teaching data collection is complete |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
taughtFeaturePts2D |
Positions of multiple taught feature points in the 2D camera coordinate system. Its value can be used as the input parameter [targetFeaturePts] for the primitive [HPImageBasedVS]. |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
taughtAlignPts2D |
Positions of the feature points of the aligned object in the 2D camera coordinate system during teaching. Its value can be used as the input parameter [alignObjPts] for the primitive [HPImageBasedVS]. |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
taughtFeaturePtsNoise |
Noise of the taught 2D feature points. Its value can be used as the input parameter [visualDetectNoise] for the primitive [HPImageBasedVS]. |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
taughtFeaturePts3D |
Positions of multiple taught feature points in the 3D camera coordinate system. Its value can be used as the input parameter [targetFeaturePts] for the primitive [HPPoseBasedVS]. |
ARRAY_VEC_3d |
m |
taughtAlignPts3D |
Positions of the feature points of the aligned object in the 3D camera coordinate system during teaching. Its value can be used as the input parameter [alignObjPts] for the primitive [HPPoseBasedVS]. |
ARRAY_VEC_3d |
m |
taughtObjPose |
Pose of the target object taught in the 3D camera coordinate system. Its value can be used as the input parameter [targetObjPose] for the primitive [HPPoseBasedVS]. |
POSE |
mm-deg |
taughtAlignPose |
Pose of the aligned object in the 3D camera coordinate system during teaching. Its value can be used as the input parameter [alignObjPose] for the primitive [HPPoseBasedVS]. |
POSE |
mm-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
teachFinished |
= |
1 |

HPImageBasedVS
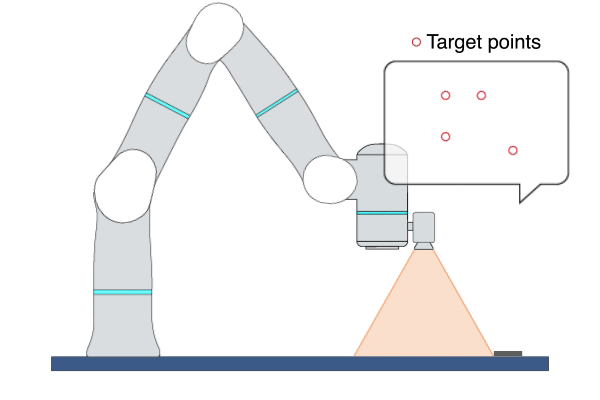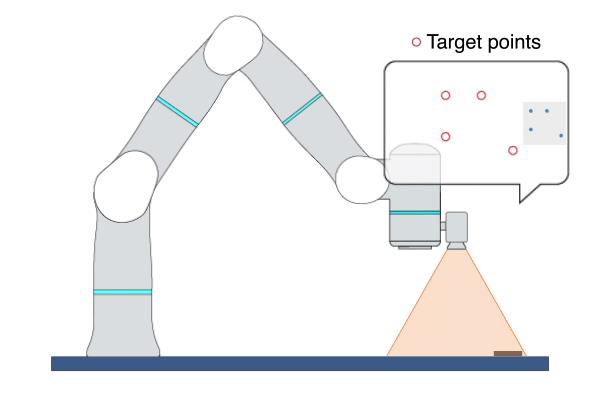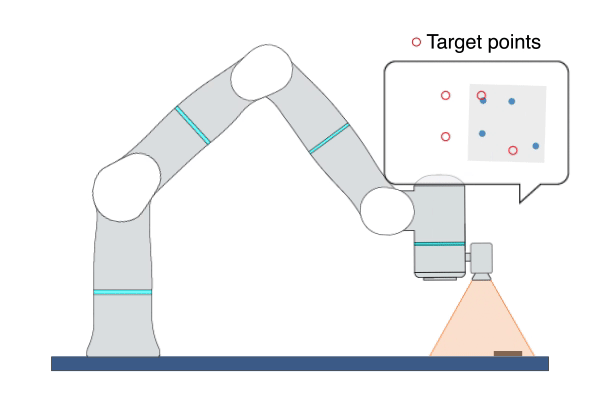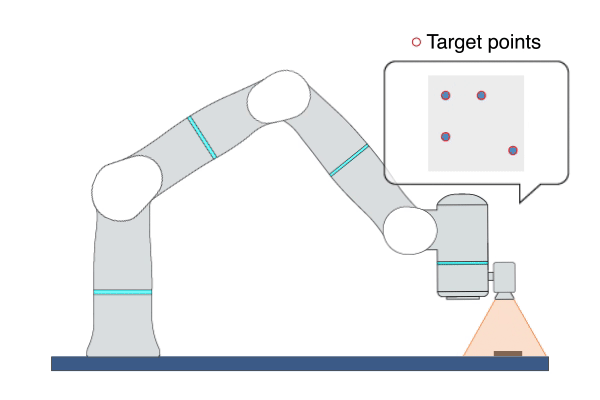
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive uses Image-Based Visual Servoing (IBVS), leveraging real-time visual feedback to continuously control the robot to track objects with random and unpredictable positions, achieving high-precision, high-responsiveness, and quasi-static tracking. During this process, the robot moves along the visual servoing axes to align the feature points on the target object with the target feature points.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to control the robot to locate an object whose position is uncertain or changing on the plane. This primitive can also be used to align two objects, such as aligning an FPC cable with a socket.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
objName* |
Object name used by visual servoing |
OBJNAME |
none |
|
objIndex |
Object index used by visual servoing |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 1] |
targetFeaturePts* |
Position of the target feature points in the 2D camera coordinate system. Each point is represented by two pixel values (X, Y). |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
|
targetDepth* |
Depth of target feature points in the camera coordinate system |
ARRAY_DOUBLE |
m |
[0.01 … 1.2] |
vsAxis |
Axes that are allowed to move in the camera coordinate system |
VEC_6i |
none |
1 1 1 0 0 1 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
velScale |
Velocity scale of visual servoing. Caution: Setting this value too large may cause robot vibration. |
DOUBLE |
none |
10 ∈ [1.0 … 100.0] |
maxVel |
Maximum linear velocity of robot movement |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.05 ∈ [0.001 … 0.5] |
maxAngVel |
Maximum angular velocity of robot movement |
DOUBLE |
deg/s |
20.0 ∈ [1.0 … 100] |
imageConvToler |
Tolerance for determining whether the image has converged. When the error between the captured image features and the target features is within the tolerance, it will be determined that convergence has occurred. |
DOUBLE |
none |
5.0 ∈ [1 … 50] |
targetConvTimes |
Number of consecutive times the target simultaneously meets the image convergence tolerances. When the number of consecutive convergences reaches this set value, the parameter [objAligned] will be set to TRUE; 0 indicates that [objAligned] will never be TRUE. |
INT |
none |
4 ∈ [0 … 20] |
timeoutTime |
Maximum time interval allowed for receiving data. A fault will be triggered if the robot fails to receive visual feedback data within this time interval. |
DOUBLE |
s |
3 ∈ [0.1 … 10] |
enableObjAlign |
Flag to enable the object alignment function. This function can be used to align the feature points of two objects. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
alignObjPts |
Position of feature points of aligned object in the 2D camera coordinate system. Each point is represented by two pixel values (X, Y). The aligned object is in the robot hand and is moved by the robot. |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
|
optVelScale |
Increase the velocity scale of visual servoing in the Z and Rz directions. It can help optimize the robot’s Cartesian motion trajectory. |
VEC_2d |
none |
0 0 ∈ [0 0 … 100 100] |
visualDetectNoise |
Noise of the visual detection result of each feature point |
ARRAY_VEC_2d |
none |
[0 0 … 20 20] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
objAligned |
Flag to indicate whether visual servoing has successfully aligned the target object |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

HPPoseBasedVS
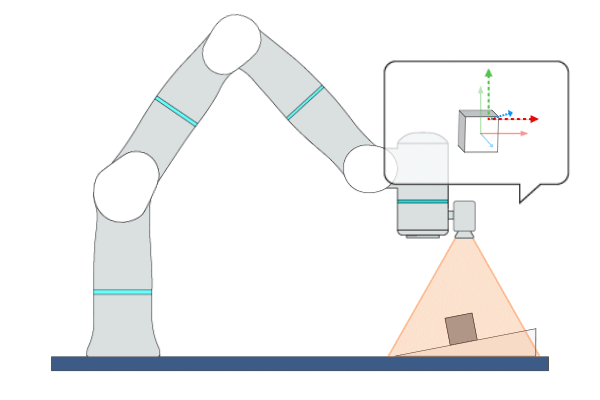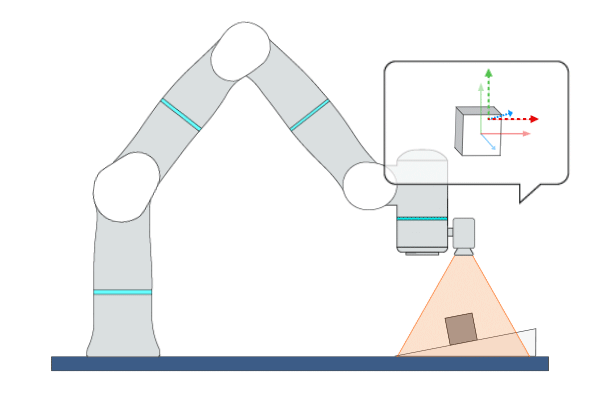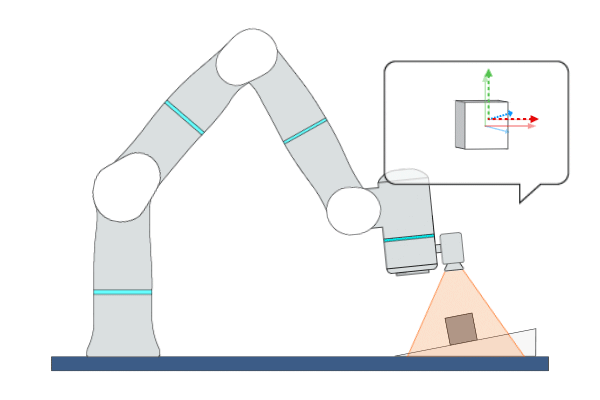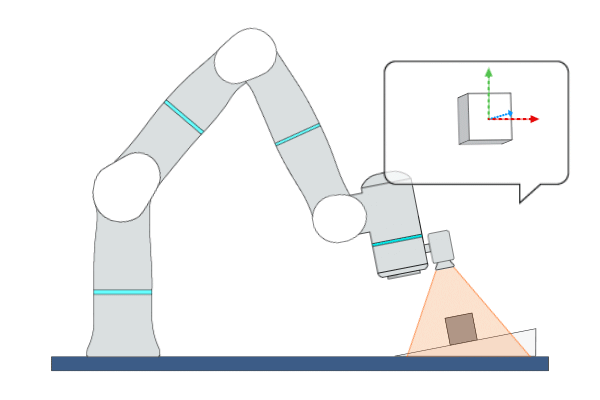
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive uses Position-Based Visual Servoing (PBVS), leveraging real-time visual feedback to continuously control the robot to track objects with random and unpredictable positions, achieving high-precision, high-responsiveness, and quasi-static tracking. During this process, the robot moves along the visual servoing axes to align the pose of the target object with the target feature points or target pose.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to control the robot to locate an object whose position and pose are uncertain in free space.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
objName* |
Object name used by visual servoing |
OBJNAME |
none |
|
objIndex |
Object index used by visual servoing |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 1] |
detectObjPose |
Flag to indicate whether visual servoing detects the object pose. If this parameter is set to TRUE, visual servoing will take the object pose as the alignment target; if this parameter is set to FALSE, visual servoing will take the feature points as the alignment target. |
BOOL |
none |
1 ∈ [0 / 1] |
targetObjPose |
Target object pose in the camera coordinate system |
POSE |
mm-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 |
vsCoord |
Reference coordinate system for visual servoing control direction |
COORD |
mm-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN ∈ [world* tcp_start* tcp*] |
vsAxis |
Axes that are allowed to move in the visual servoing coordinate system |
VEC_6i |
none |
1 1 1 1 1 1 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
velScale |
Velocity scale of visual servoing axes. Caution: Setting this value too large may cause robot vibration. |
VEC_6d |
none |
10 10 10 10 10 10 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0] |
maxVel* |
Maximum linear velocity and angular velocity allowed for the robot to move in each direction of the visual servoing coordinate system. |
VEC_6d |
none |
0.1 0.1 0.1 10.0 10.0 10.0 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 … 0.5 0.5 0.5 100.0 100.0 100.0] |
maxAcc* |
Maximum linear acceleration and angular acceleration allowed for the robot to move in each direction of the visual servoing coordinate system. |
VEC_6d |
none |
2.5 2.5 2.5 300.0 300.0 300.0 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 … 5.0 5.0 5.0 600.0 600.0 600.0] |
timeoutTime |
Maximum time interval allowed for receiving data. A fault will be triggered if the robot fails to receive visual feedback data within this time interval. |
DOUBLE |
s |
3 ∈ [0.1 … 10] |
visualDelayTime |
Time interval between the image captured by the camera and the image received by visual servoing |
DOUBLE |
s |
0 ∈ [0.0 … 0.5] |
posConvToler |
Tolerance for determining whether the position has converged. When the error between the captured feature position and the target feature position is within the tolerance, it will be determined that convergence has occurred. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.001 ∈ [0.0001 … 0.01] |
rotConvToler |
Tolerance for determining whether the rotation has converged. When the error between the rotation angle of the captured feature and the rotation angle of the target feature is within the tolerance, it will be determined that convergence has occurred. |
DOUBLE |
deg |
1 ∈ [0.01 … 10] |
targetConvTimes |
Number of consecutive times the target simultaneously meets both the position and rotation convergence tolerances. When the number of consecutive convergences reaches this set value, the parameter [objAligned] will be set to TRUE; 0 indicates that [objAligned] will never be TRUE. |
INT |
none |
3 ∈ [0 … 20] |
targetFeaturePts |
Position of the target feature points in the 3D camera coordinate system. Each point is represented by three coordinate values (X, Y, Z). At least 3 feature points are required to represent the object pose. |
ARRAY_VEC_3d |
m |
|
enableObjAlign |
Flag to enable the object alignment function. This function can be used to align the feature points of two objects. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
alignObjPts |
Position of feature points of aligned object in the 3D camera coordinate system. Each point is represented by three values (X, Y, Z). The aligned object is in the robot hand and is moved by the robot. |
ARRAY_VEC_3d |
m |
|
alignObjPose |
Pose of aligned object in the 3D camera coordinate system. The aligned object is in the robot hand and is moved by the robot. |
POSE |
mm-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 |
suppressOvershoot |
Flag to indicate whether visual servoing suppresses the position overshoot. If this parameter is set to TRUE, visual servoing will apply an overshoot suppression mechanism to the position control; the robot will operate more stably when executing visual servoing tasks, but the response speed may slow down accordingly. If this parameter is set to FALSE, the control system will run without overshoot suppression. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
dynamicObjTrack |
Flag to indicate whether dynamic object tracking is enabled. If this parameter is set to TRUE, visual servoing will achieve better tracking performance for objects moving at a constant velocity, but may result in a slower convergence speed for static objects. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
visDetectNoiseLevel |
Noise level of the visual detection result of object pose. It ranges from 1 to 100, where 1 means the smallest noise. |
INT |
none |
1 ∈ [1 … 100] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
objAligned |
Flag to indicate whether visual servoing has successfully aligned the target object |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

HPOffsetServo
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive uses Offset-Based Visual Servoing (OBVS), leveraging real-time visual feedback to continuously control the robot to track objects with random and unpredictable positions, achieving high-precision, high-responsiveness, and quasi-static tracking. During this process, the robot moves to the specified target pose while continuously adjusting the pose of the target object along the visual servoing axes.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to control the robot to dynamically calibrate its pose while moving to the target pose. The host needs to continuously send the pose offset to this primitive, so that real-time adjustment of the object’s pose can be achieved.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
objName* |
Object name used by visual servoing |
OBJNAME |
none |
|
objIndex |
Object index used by visual servoing |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 1] |
target |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
mm-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN ∈ [traj_start* world*] |
vsCoord |
Reference coordinate system for visual servoing control direction |
COORD |
mm-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN ∈ [world* tcp_start* tcp*] |
vsAxis |
Axes that are allowed to move in the visual servoing coordinate system |
VEC_6i |
none |
1 1 1 1 1 1 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
velScale |
Velocity scale of visual servoing axes. Caution: Setting this value too large may cause robot vibration. |
VEC_6d |
none |
10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0] |
maxVel* |
Maximum linear velocity and angular velocity allowed for the robot to move in each direction of the visual servoing coordinate system. |
VEC_6d |
none |
0.1 0.1 0.1 10.0 10.0 10.0 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 … 0.5 0.5 0.5 100.0 100.0 100.0] |
maxAcc* |
Maximum linear acceleration and angular acceleration allowed for the robot to move in each direction of the visual servoing coordinate system. |
VEC_6d |
none |
2.5 2.5 2.5 300.0 300.0 300.0 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 … 5.0 5.0 5.0 600.0 600.0 600.0] |
timeoutTime |
Maximum time allowed for data interval |
DOUBLE |
s |
1 ∈ [0.1 … 10] |
visualDelayTime |
Maximum time interval allowed for receiving data. A fault will be triggered if the robot fails to receive visual feedback data within this time interval. |
DOUBLE |
s |
0 ∈ [0.0 … 0.5] |
posConvToler |
Tolerance for determining whether the position has converged. When the error between the captured feature position and the target feature position is within the tolerance, it will be determined that convergence has occurred. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.001 ∈ [0.0001 … 0.01] |
rotConvToler |
Tolerance for determining whether the rotation has converged. When the error between the rotation angle of the captured feature and the rotation angle of the target feature is within the tolerance, it will be determined that convergence has occurred. |
DOUBLE |
deg |
1 ∈ [0.01 … 10] |
targetConvTimes |
Number of consecutive times the target simultaneously meets both the position and rotation convergence tolerances. When the number of consecutive convergences reaches this set value, the parameter [objAligned] will be set to TRUE; 0 indicates that [objAligned] will never be TRUE. |
INT |
none |
3 ∈ [0 … 20] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
objAligned |
Flag to indicate whether visual servoing has successfully aligned the target object |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |
