Basic Force Control
ZeroFTSensor
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive is used to reset the Cartesian force/torque offset to zero. It is usually used before force control primitives. This primitive can be used for all Flexiv robots, including those with a 6DoF sensor. The robot should be static enough (i.e. the previous primitive cannot trigger extremely aggressive motions) when entering this primitive. During the calibration, the robot should neither be touched nor contact with the environment.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to reset the Cartesian force/torque offset (to zero) before polishing or contacts.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
dataCollectTime |
The amount of time used to collect force/torque offset prior to resetting the FT sensor |
DOUBLE |
s |
0.2 ∈ [0.1 … 1.0] |
enableStaticCheck |
Enable checking if the robot is static or not |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
calibExtraPayload |
Flag to indicate whether the extra payload is accounted for in the end-of-arm tool payload during force/torque calibration |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
terminated |
= |
1 |

Contact
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive maintains force control and moves the robot in a predefined direction with a set force until it contacts with the environment. The robot stops immediately when its contact force with the object reaches the set max contact force value. Primitive [ZeroFTSensor] should always be used before executing this primitive.
Example Usage: Use this primitive when the robot performs tasks that require contact with the environment. For example, use this primitive to make robot’s tool contact with the parts before performing polishing or peg-in-hole tasks.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
contactCoord |
Reference coordinate system for the contact direction |
TYPE |
none |
world ∈ [world tcp general] |
generalContactCoord |
If the parameter [contactCoord] is set to “general”, this parameter will be used as the reference coordinate system for the contact direction |
COORD |
m-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN ∈ [traj_start* traj_prev* world*] |
contactDir |
Approaching direction toward the contact surface in the contact coordinate system |
VEC_3d |
none |
0.0 0.0 -1.0 |
contactVel |
TCP linear velocity while moving to contact |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.02 ∈ [0.001 … 0.1] |
maxContactForce |
Maximum contact force. The primitive will be terminated when external force exceeds this limit. |
DOUBLE |
N |
5.0 ∈ [1.0 … 120] |
enableFineContact |
Enabling this mode allows the robot to automatically adjust the velocity upon contact; otherwise, the robot will only move at a constant velocity |
BOOL |
none |
1 ∈ [0 / 1] |
waypoint |
Waypoint pose |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_prev* world*] |
vel |
TCP linear velocity |
ARRAY_DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.02 ∈ [0.001 … 2.2] |
acc |
TCP linear acceleration |
ARRAY_DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
1.5 ∈ [0.1 … 3.0] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius when TCP approaches the waypoint |
ARRAY_TYPE |
none |
[ZFine Z1 Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200] |
jerk |
TCP linear jerk |
DOUBLE |
m/s^3 |
50.0 ∈ [50.0 … 1000.0] |
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
curContactForce |
Current force in the contact direction |
DOUBLE |
N |
forwardDis |
Forward distance from the start position to the contact point |
DOUBLE |
m |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
terminated |
= |
1 |

ForceHybridLite
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive controls the robot TCP to move linearly through waypoints to the target pose in hybrid motion/force control mode, while applying a constant force in the TCP direction. It is the basic version of the primitive [ForceHybrid]. You can use [ForceHybrid] for more versatile and safer force control performance.
Example Usage: Use this primitive for better hybrid motion/force control performance when the robot needs to apply a constant external force while running a trajectory.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
waypoint |
Waypoint pose |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
vel |
TCP linear velocity |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.25 ∈ [0.001 … 2.2] |
acc |
TCP linear acceleration |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
10 ∈ [0.1 … 15.0] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius when TCP approaches the waypoint |
TYPE |
none |
Z50 ∈ [ZFine Z1 Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 10] |
forceAxis* |
Activated axes of force control coordinate system to apply force or torque |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 0 1 0 0 0 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 0 0 0] |
targetWrench* |
Target force and torque applied to the robot’s running trajectory |
VEC_6d |
N |
0.0 0.0 -5.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 |
jerk |
TCP linear jerk |
DOUBLE |
m/s^3 |
50.0 ∈ [50.0 … 1000.0] |
stiffScale |
Robot stiffness scale during motion. The lower the stiffness scale, the more compliant the motion. |
VEC_6d |
none |
1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ∈ [0.01 0.01 0.01 0.0 0.0 0.0 … 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0] |
maxVelForceDir |
Maximum movement velocity along force control direction |
VEC_3d |
m/s |
2.0 2.0 2.0 ∈ [0.005 0.005 0.005 … 2.0 2.0 2.0] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate whether the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

ForceCompLite
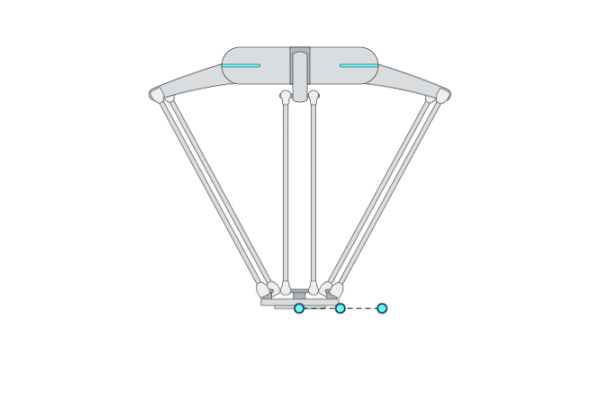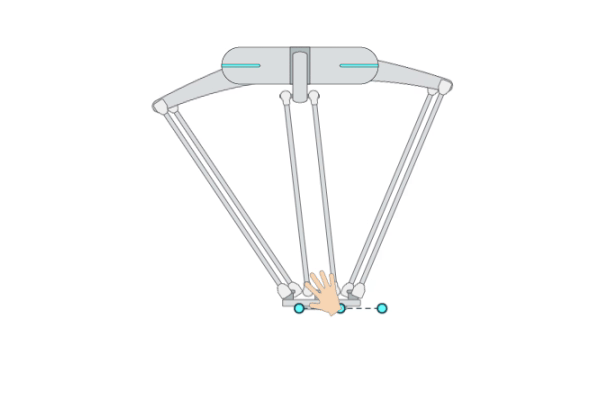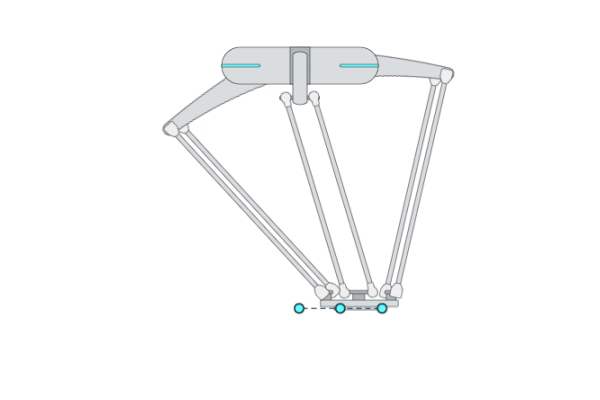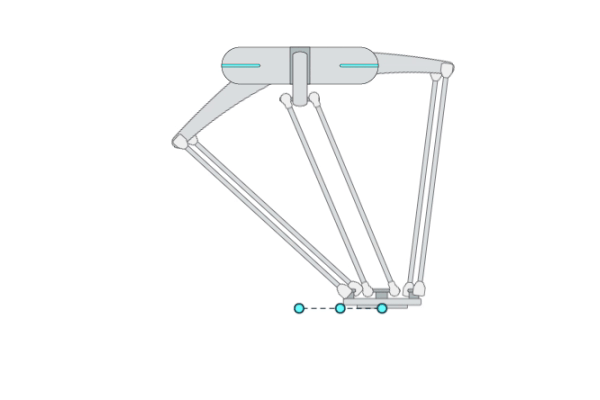
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive compliantly moves the robot TCP to a target pose while passing through multiple waypoints. It is the basic version of the primitive [ForceComp]. You can use [ForceComp] for more precise compliant motion control performance.
Example Usage: Use this primitive when the robot has a chance to collide with an unknown environment during Cartesian movement or when you want to compliantly interact with the robot during movement. You can also use primitive [ForceComp] for better compliant motion performance.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
waypoints |
Waypoints between initial and target poses |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius when TCP approaches the waypoint |
TYPE |
none |
Z50 ∈ [ZFine Z1 Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 10] |
vel |
TCP linear velocity |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.25 ∈ [0.001 … 2.2] |
compAxis |
Compliant axis in compliance coordinate system |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 0 0 0 0 0 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 0 0 0] |
acc |
TCP linear acceleration |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
10 ∈ [0.1 … 15.0] |
jerk |
TCP linear jerk |
DOUBLE |
m/s^3 |
50.0 ∈ [50.0 … 1000.0] |
compCoord |
Reference coordinate system for the compliant motion |
COORD |
m-deg |
0 0 0 0 0 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN ∈ [world* tcp_start* tcp*] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
Flag to indicate whether the primitive is terminated. It is set to TRUE if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate whether the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |
