Adaptive Assembly
SearchHole
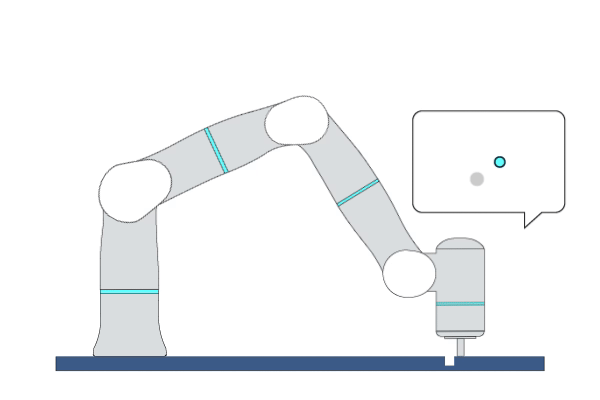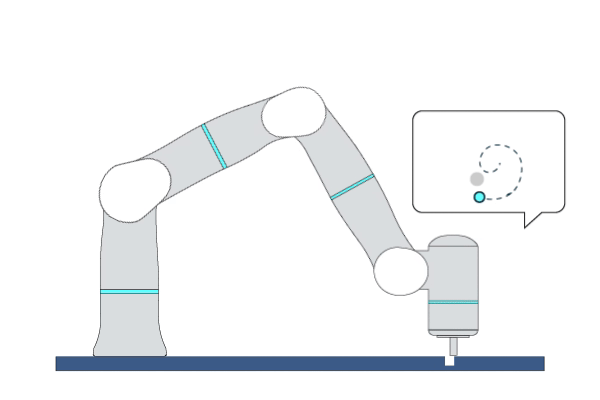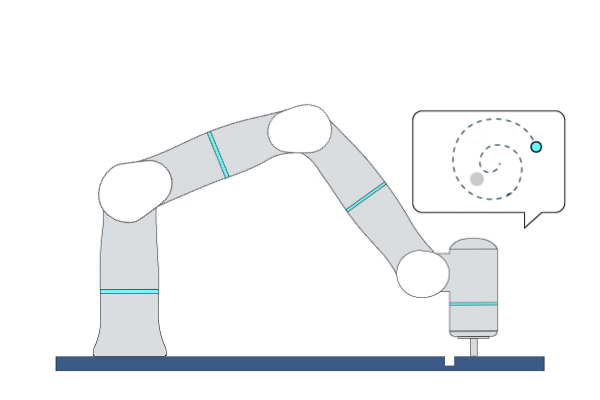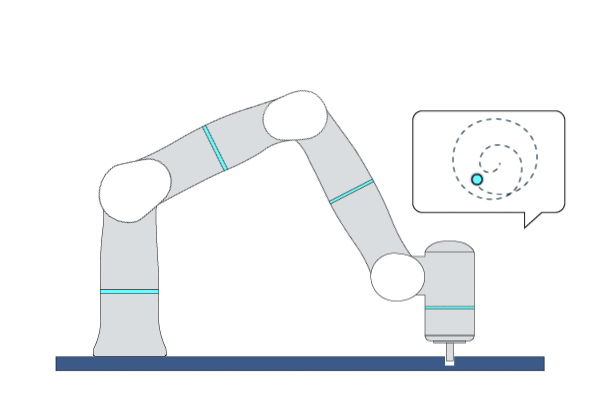
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive provides a force-search mechanism to control the robot to find the hole in peg-in-hole assembly tasks. Specifically, it controls the robot to search along an increasingly dense trajectory within a circular or rectangular area on a surface while maintaining a certain contact force.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to position the hole before performing the peg-in-hole assembly tasks.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
contactAxis |
Contact (force control) direction in TCP coordinate system, which should be along one of TCP’s principal axes [X, Y, Z] |
VEC_3d |
none |
0.0 0.0 1.0 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 … 1.0 1.0 1.0] |
contactForce |
Contact force when searching on the surface |
DOUBLE |
N |
5 ∈ [2 … 20] |
searchAxis |
Search direction in TCP coordinate system, which should be perpendicular to the contact axis |
VEC_3d |
none |
1.0 0.0 0.0 |
searchPattern |
Pattern formed by the searching trajectory (spiral or zigzag) |
TYPE |
none |
SPIRAL ∈ [SPIRAL ZIGZAG] |
spiralRadius |
Searching area radius of spiral search pattern; when payload or contact surface friction/resistance is large, this value might be slightly smaller than its nominal value. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.015 ∈ [0.001 … 0.015] |
zigzagLength |
Searching area length of zigzag search pattern along the search axis; when payload or contact surface friction/resistance is large, this value might be slightly smaller than its nominal value. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.03 ∈ [0.001 … 0.03] |
zigzagWidth |
Searching area width of zigzag search pattern, which is perpendicular to the search and contact axis; when payload or contact surface friction/resistance is large, this value might be slightly smaller than its nominal value. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.03 ∈ [0.001 … 0.03] |
startDensity |
Number of times the geometry pattern will be drawn in the start cycle |
INT |
none |
2 ∈ [1 … 5] |
timeFactor |
Time factor for how long it takes for TCP to form a pattern. Caution: 1. Small time factor for a large search radius may cause the robot to exceed its capabilities and stop. 2. In Manual mode, this factor is approximately doubled regardless of the speed percentage. |
INT |
none |
2 ∈ [1 … 10] |
wiggleRange |
Range for TCP to wiggle along the contact axis to find the right angle during searching. Caution: If this parameter is set to a large value, make sure to increase the wigglePeriod, otherwise, the robot may exceed its capabilities. |
DOUBLE |
deg |
0 ∈ [0 … 90] |
wigglePeriod |
Time period for TCP to wiggle along the contact axis back and forth once. Caution: 1. Setting this value too small will likely cause the robot exceeding its capabilities and stop, especially when the wiggle motion is not along the Z-axis of the robot flange. 2. in manual mode, this factor is approximately doubled regardless of the speed percentage. |
DOUBLE |
s |
0.3 ∈ [0.2 … 30] |
enableMaxWrench |
Flag to indicate if maximum contact wrench is enabled in each Cartesian direction: X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 0 0 0 0 0 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
maxContactWrench |
Maximum contact wrench allowed for static collision along Fx, Fy, Fz, Mx, My, Mz |
VEC_6d |
N |
150.0 150.0 150.0 40.0 40.0 40.0 ∈ [5.0 5.0 5.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 … 150.0 150.0 150.0 40.0 40.0 40.0] |
searchImmed |
Start searching immediately without waiting for contact force to reach its set value |
BOOL |
none |
1 ∈ [0 / 1] |
searchStiffRatio |
Factor of the stiffness during searching motion. Caution: Setting this value too small, the robot may not follow the searching trajectory very well, especially when the surface friction or contact force is very large. |
DOUBLE |
none |
1 ∈ [0.1 … 1] |
maxVelForceDir |
Maximum movement velocity along force control direction |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.1 ∈ [0.005 … 0.5] |
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
searchResisForce |
Feedback force during searching motion, which could indicate the collision or resistance. |
DOUBLE |
N |
pushDis |
Pushed distance of TCP into the surface, which could signal a successful find. |
DOUBLE |
m |
forceDrop |
Dropped value from the set contact force. Caution: this state will not be reliable if input parameter [searchImmed] is set to TRUE. |
DOUBLE |
N |
lostContact |
Flag to indicate the loss of contact. This flag will only be switched on when the forces detected on all X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz axes are smaller than 1N or 1Nm for 1.5 consecutive seconds. |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
pushDistance |
> |
0.005 |

CheckPiH
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive helps check if a peg is already in a hole. You can specify a contact axis and a search axis perpendicular to the contact axis, and a companion axis will be generated to form a frame. The robot will move toward the +searchAxis, -searchAxis, -companionAxis, +companionAxis. While moving along these axes, if the robot goes over the limit specified by [searchRange], the primitive will terminate and the state parameter [pegIsInHole] will be set to false; if the robot encounters a force greater than [searchForce] along all these directions during the process, the primitive will terminate and [pegIsInHole] will be set to true.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to check if a peg-in-hole operation is completed.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
contactAxis |
Contact (force control) direction in TCP coordinate system, which should be along one of TCP’s principal axes [X, Y, Z] |
VEC_3d |
none |
0.0 0.0 1.0 |
searchAxis |
Search direction in TCP coordinate system, which should be perpendicular to the contact axis |
VEC_3d |
none |
1.0 0.0 0.0 |
searchRange |
Range within which the robot will make forward, backward, left, and right search motions |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.01 ∈ [0.001 … 0.1] |
searchForce |
Force threshold to detect if the robot can move along the searching direction. Robot will move along the next motion direction when detected force is greater than this value. |
DOUBLE |
N |
3 ∈ [2 … 20] |
searchVel |
TCP linear velocity for the searching motion |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.01 ∈ [0.001 … 0.1] |
linearSearchOnly |
Flag to indicate if the robot only searches linearly in the direction of +searchAxis and -searchAxis |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
returnToInitPose |
Flag to indicate if the robot would return to initial pose when check is failed |
BOOL |
none |
true ∈ [0 / 1] |
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
pegIsInHole |
Flag to indicate if the peg is already in the hole |
BOOL |
none |
checkComplete |
Flag to indicate if the peg-in-hole check is complete |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
initTcpPose |
Initial TCP pose when the project runs to this primitive |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
checkComplete |
= |
1 |

InsertComp
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive moves the robot in a predefined insertion direction until the total external force reaches a set value. During the insertion process, if there is an external force in directions other than the insertion direction that exceeds the deadband, the robot will stop the insertion motion and adjust its position and orientation in the corresponding direction until the forces in all directions are within the deadband.
Example Usage: Use this primitive in fine assembly tasks such as gearbox assembly, peg-in-hole assembly, or in machine tending applications like putting a sleeve (a hollow cylinder) on a shaft.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
insertAxis* |
Insertion direction in TCP coordinate system |
TYPE |
none |
[X -X Y -Y Z -Z] |
compAxis |
Force compliance axes in TCP coordinate system. The robot performs compliant motion along the axis whose value is set to 1. |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 0 0 0 0 0 ∈ [0 0 0 0 0 0 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
maxContactForce |
Maximum contact force. The primitive will be terminated when external force exceeds this limit. |
DOUBLE |
N |
5 ∈ [1 … 120] |
deadbandScale |
Deadband scale of applied alignment wrench. The robot only performs compliant motion when the external wrench is higher than this deadband. 0 means no deadband. |
DOUBLE |
none |
50 ∈ [10 … 100] |
insertVel |
TCP Linear velocity in insertion direction |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.01 ∈ [0.001 … 0.1] |
compVelScale |
Velocity scale of compliant motion. Higher velocity scale results in faster but less stable compliant motion. |
DOUBLE |
none |
20 ∈ [10 … 100] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
insertDis |
Robot moving distance in the insertion direction |
DOUBLE |
m |
isMoving |
Flag to indicate if robot is still moving |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
isMoving |
= |
0 |

Mate
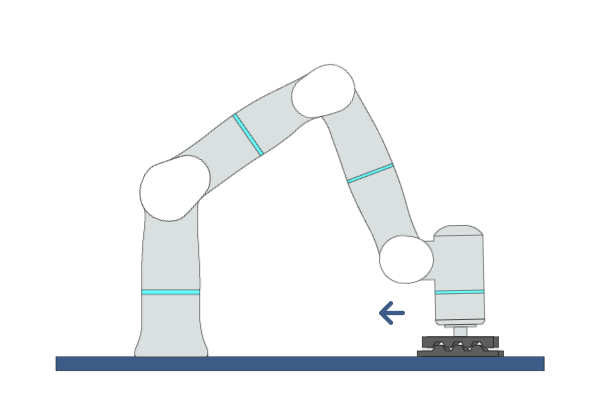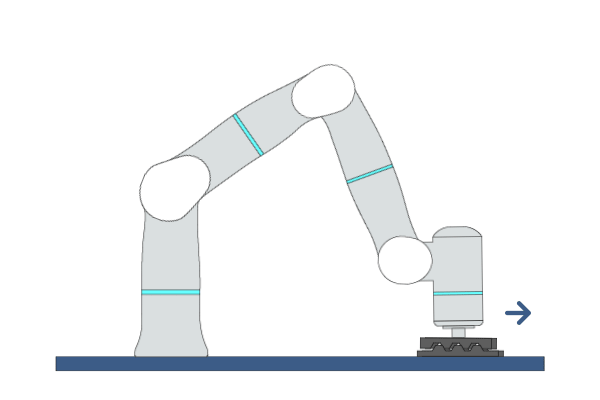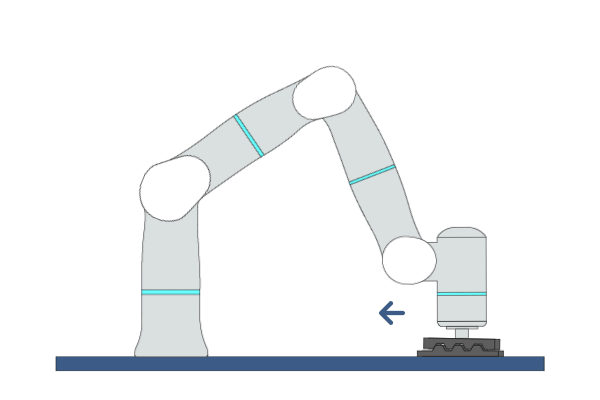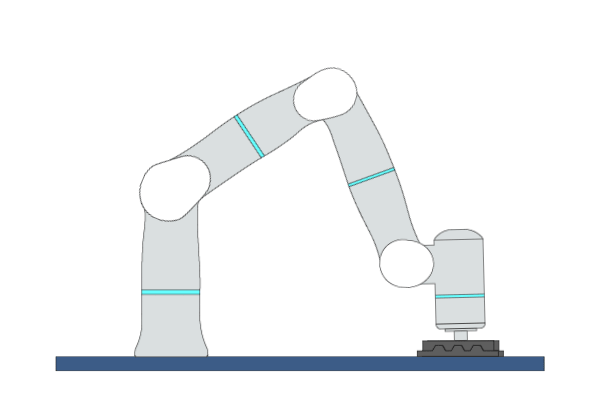
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive moves the robot back and forth in one direction while applying a certain force in a specific direction until mating is complete. The mating success rate can be improved by adding mating motion in another direction.
Example Usage: Use this primitive for parts mating in assembly tasks.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
contactAxis |
Contact (force control) direction in TCP coordinate system, which should be along one of TCP’s principal axes [X, Y, Z] |
VEC_3i |
none |
0 0 1 ∈ [-1 -1 -1 … 1 1 1] |
contactForce |
Target force along the contact axis |
DOUBLE |
N |
15 ∈ [5 … 50] |
matingAxis |
An axis in TCP coordinate system representing the sliding or rotating direction during mating, which should not be the same as contact axis |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 1 0 0 0 0 ∈ [-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
slideMatingRange |
Sliding mating motion range |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.1 ∈ [0.001 … 0.35] |
slideMatingVel |
TCP linear velocity of sliding mating motion |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.1 ∈ [0.001 … 0.5] |
slideMatingAcc |
TCP linear acceleration of sliding mating motion |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
1.0 ∈ [0.1 … 2.5] |
rotateMatingRange |
Rotating mating motion range |
DOUBLE |
deg |
10 ∈ [1 … 60] |
rotateMatingVel |
TCP angular velocity of rotating mating motion |
DOUBLE |
deg/s |
10 ∈ [1.0 … 60.0] |
rotateMatingAcc |
TCP angular acceleration of rotating mating motion |
DOUBLE |
deg/s^2 |
180 ∈ [5 … 500] |
matingTimes |
Total number of mating times. The primitive will be terminated when the specified number of times of mating motion is reached. Caution: If set to 0, the robot performs ONLY forward motion once. |
INT |
none |
1 ∈ [0 … 1000] |
maxContactDis |
Maximum moving distance along contact axis. The primitive will be terminated when the moving distance exceeds this value. |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.05 ∈ [0.005 … 0.5] |
safetyForce |
Safety force limit during mating. The primitive will be terminated when the feedback force exceeds this value. |
DOUBLE |
N |
50.0 ∈ [20 … 80] |
addMatingAxis |
An additional axis in TCP coordinate system representing the sliding or rotating direction during mating, which should not be the same as contact axis or mating axis. The additional mating motion along this axis will be superimposed on the mating motion. |
VEC_6i |
none |
0 0 0 0 0 0 ∈ [-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 … 1 1 1 1 1 1] |
addSlideMatingRange |
Additional sliding mating motion range |
DOUBLE |
m |
0.05 ∈ [0.001 … 0.1] |
addSlideMatingVel |
TCP linear velocity of additional sliding mating motion |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.1 ∈ [0.001 … 0.5] |
addSlideMatingAcc |
TCP linear acceleration of additional sliding mating motion |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
1.0 ∈ [0.1 … 2.5] |
addRotateMatingRange |
Additional rotating mating motion range |
DOUBLE |
deg |
10 ∈ [1 … 60] |
addRotateMatingVel |
TCP angular velocity of additional rotating mating motion |
DOUBLE |
deg/s |
10 ∈ [1.0 … 60.0] |
addRotateMatingAcc |
TCP angular acceleration of additional rotating mating motion |
DOUBLE |
deg/s^2 |
180 ∈ [5 … 500] |
maxVelForceDir |
Maximum movement velocity along force control direction. It constrains the robot’s speed in cases where the robot suddenly loses contact with the environment. Note that if its value is set too small, the robot’s force control performance may degrade. |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.5 ∈ [0.002 … 0.5] |
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
matingFinish |
Flag to indicate if the mating process is finished |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
matingFinished |
= |
1 |

FastenScrew
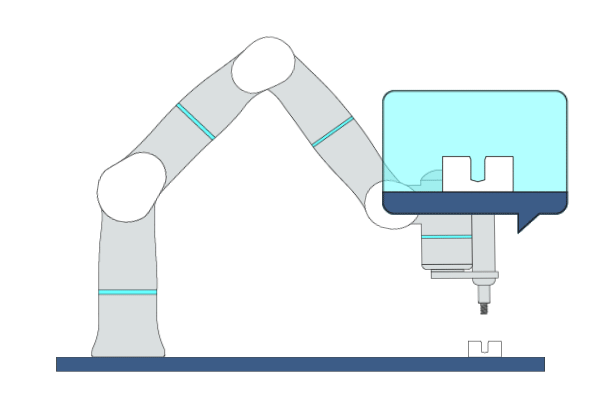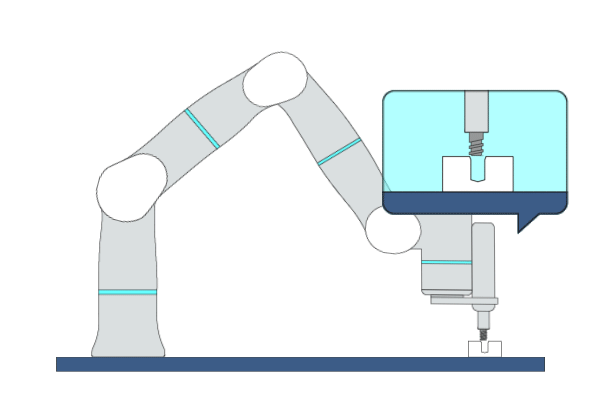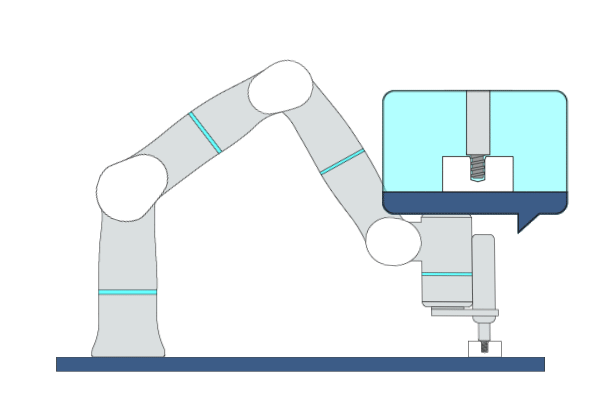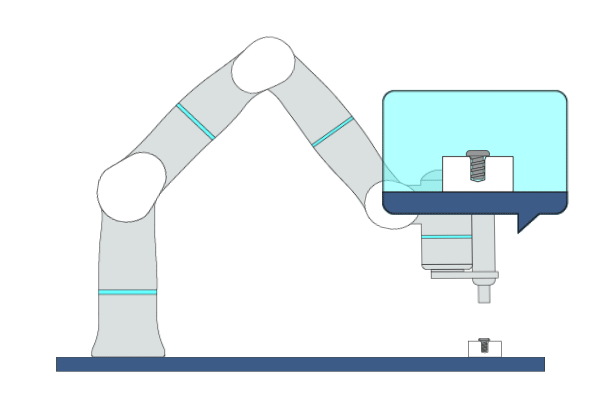
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive is applicable to screw fastening tasks. During the fastening process, the robot maintains contact with objects along the insertion direction while performing compliant motion in other directions.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to fasten the screws in assembly applications.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
insertDir |
Screw insertion direction in TCP coordinate system |
TYPE |
none |
Z ∈ [X -X Y -Y Z -Z] |
maxInsertVel |
Maximum screw insertion velocity into the screw hole |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.01 ∈ [0.001 … 0.05] |
insertForce |
Screw insertion force during fastening process |
DOUBLE |
N |
20 ∈ [10 … 50] |
stiffScale |
Robot stiffness scale while fastening the screw. Lower scale applies higher motion compliance. |
DOUBLE |
none |
0.5 ∈ [0.1 … 1] |
diScrewInHole |
Digital input port which receives the signal from screw gun, indicating that screw has been tightened a bit into the screw hole. |
TYPE |
none |
NONE ∈ [NONE, gpioIn0 … gpioIn15, modbusIn0 … modbusIn15] |
diFastenFinish |
Digital input port which receives the signal from screw gun, indicating that screw has been totally tightened. |
TYPE |
none |
NONE ∈ [NONE, gpioIn0 … gpioIn15, modbusIn0 … modbusIn15] |
diScrewJam |
Digital input port which receives the signal from screw gun, indicating that screw has been jammed. |
TYPE |
none |
NONE ∈ [NONE, gpioIn0 … gpioIn15, modbusIn0 … modbusIn15] |
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
insertDis |
Screw insertion distance into the screw hole |
DOUBLE |
m |
insertVel |
Screw insertion velocity into the screw hole |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
fastenState |
Screw fastening state: 0 means default state; 1 means screw has been tightened a bit into the screw hole; 2 means screw has been totally tightened; -1 means screw has been jammed. |
INT |
none |
reachedHole |
Flag to indicate screw has reached full contact with screw hole |
BOOL |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
fastenState |
= |
2 |
