Showcase
BalanceBall
Primitive Description and Usage
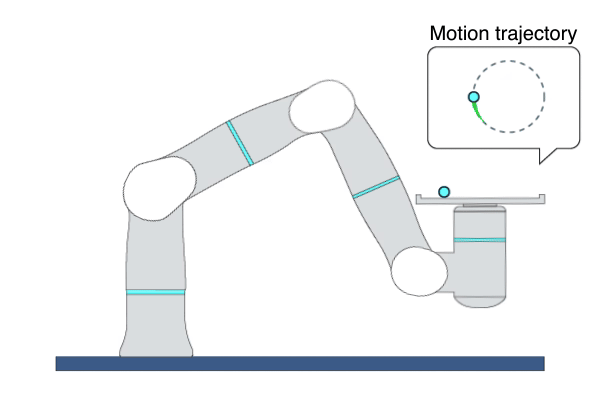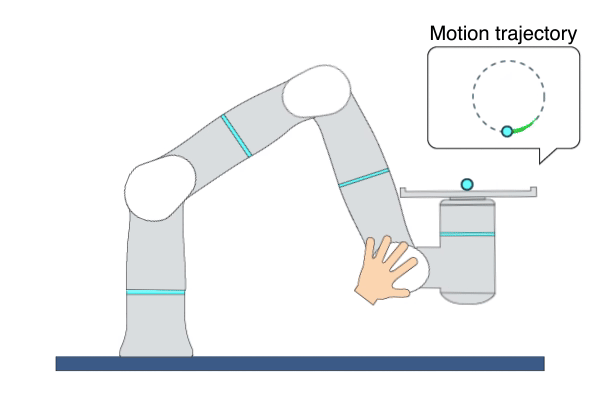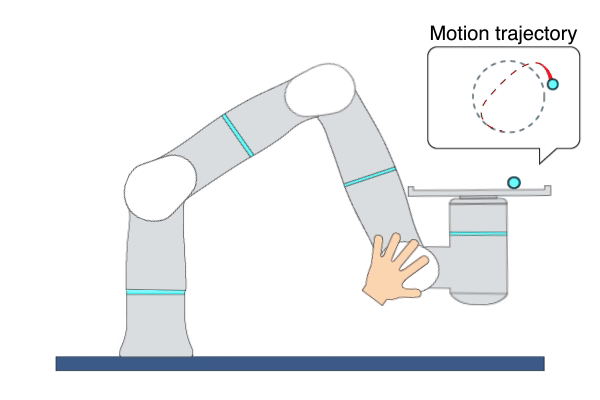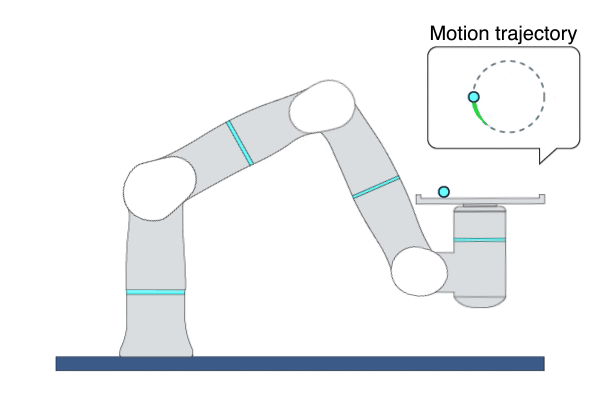
Description: This primitive demonstrates a ball-balancing task. The primitive is robust enough to run different types of sphere-shaped objects. Three types of balls are used for the Flexiv demonstration. 1) Small steel ball - weight: 0.19 kg, friction: 1.471; 2) Large steel ball - weight: 0.3 kg, friction: 1.424; 3) Galaxy ball - weight: 0.6kg, friction 1.201.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to showcase the outstanding performance of Rizon 4s and Rizon 10s.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ballWeight* |
Weight of the ball. It’s recommended to use a ball heavier than 0.25kg. |
DOUBLE |
kg |
[0.25 … 2.5] |
ballFricCoeff* |
Ball rolling friction coefficient |
DOUBLE |
none |
[1.0 … 2.5] |
pattenType |
Type of the ball rolling trajectory pattern |
TYPE |
none |
CIRCLE ∈ [CIRCLE INFSHAPE] |
COPOffsetX* |
COP (center of pressure) offset in x direction |
DOUBLE |
m |
[-0.1 … 0.1] |
COPOffsetY* |
COP (center of pressure) offset in y direction |
DOUBLE |
m |
[-0.1 … 0.1] |
pattenSizeScale |
Scale of ball rolling trajectory pattern size |
DOUBLE |
none |
1 ∈ [1 … 3] |
freScale |
Scale of ball rolling frequency to form a pattern |
DOUBLE |
none |
1 ∈ [0.3 … 1] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
timePeriod |
> |
3000 |

BalanceGlasses
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive demonstrates a wine glasses balancing task. The robot’s balancing pose is adjusted in real time in accordance with the gravitational state of the wine glasses on the tray and the liquid within. The robot TCP moves through each waypoint to reach the target point while keeping the liquid in the wine glasses from spilling. Before executing this primitive, please make sure the robot flange is facing upwards and the tray is placed horizontally. This primitive should be executed in Auto mode.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to showcase the outstanding force control performance of Rizon adaptive robots.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP position and the horizontal rotating angle (Rz). TCP pose remains horizontal during robot motion (Rx and Ry are not considered). |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
duration |
Duration of the whole motion |
DOUBLE |
s |
10.0 ∈ [0.5 … 100] |
waypoints |
Waypoints between initial and target position. TCP pose remains horizontal during robot motion (Rx and Ry are not considered). |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
0 ∈ [0 … 10] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate if the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |
