Motion
MoveL
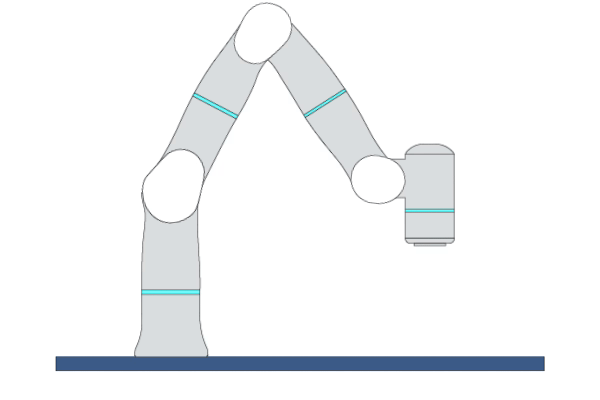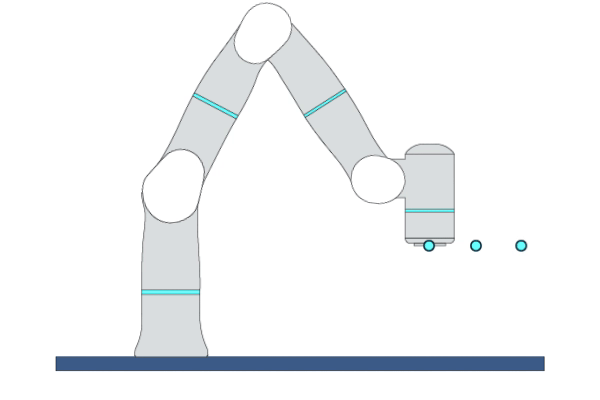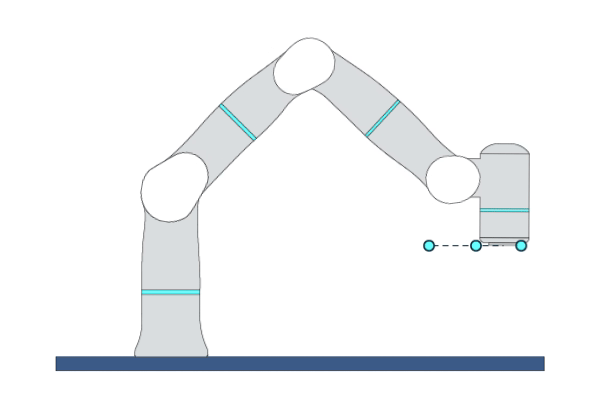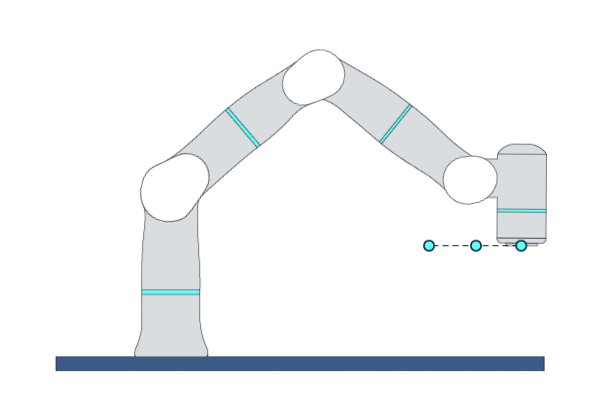
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive controls the robot TCP to move linearly to the target pose. You can specify multiple waypoints before the target point, and TCP will move in a straight line through each waypoint to reach the target point with a certain blending zone radius.
Example Usage: When the motion trajectory is required, use this primitive to move the robot TCP to the target pose along the specified trajectory.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
waypoints |
Waypoints between initial and target poses |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
vel |
TCP linear velocity |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.25 ∈ [0.001 … 2.2] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius while TCP approximates the waypoints |
TYPE |
none |
Z50 ∈ [ZFine Z1 Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
3 ∈ [0 … 10] |
acc |
TCP linear acceleration |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
1.5 ∈ [0.1 … 3.0] |
angVel |
TCP angular velocity |
DOUBLE |
deg/s |
150.0 ∈ [10.0 … 500.0] |
enableFixRefJntPos |
Flag to indicate if fixed reference joint position is enabled. If this parameter is set to TRUE, the primitive will use the value of parameter [refJntPos] as the fixed joint reference position instead of the reference joint position of each waypoint during execution. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
refJntPos |
Reference target joint positions. When the robot moves in Cartesian space, each joint will move as close as possible toward the reference position. |
JPOS |
deg |
0.0 -40.0 0.0 90.0 0.0 40.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 |
jerk |
TCP linear jerk |
DOUBLE |
m/s^3 |
50.0 ∈ [50.0 … 500.0] |
configOptObj |
Weights of three configuration optimization objectives during robot motion, which respectively are to make the robot easier to translate in Cartesian space, easier to rotate in Cartesian space, and closer to the reference joint position. |
VEC_3d |
none |
0.0 0.0 0.5 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.1 … 1.0 1.0 1.0] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
*Robot Joint Position Description
The complete description of a joint waypoint (JPOS) is: A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the positions of external axes. You can only set the robot joint positions if external axes do not exist. For example: {jnt_def_1}.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: {jnt_def_2}.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate if the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

MoveJ
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive moves the robot to the target joint position by joint movement. You can specify multiple joint waypoints before the target point, and the robot will move in a non-linear way through each waypoint to reach the target point.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to quickly move the robot to the specified joint positions in an obstacle-free space.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target joint position |
JPOS |
deg |
|
waypoints |
Waypoints between initial and target poses |
ARRAY_JPOS |
deg |
|
jntVelScale |
Robot joint velocity scale. The robot joints will move at full speed when this value is set to 100. |
INT |
none |
20 ∈ [1 … 100] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius while TCP approximates the waypoints |
TYPE |
none |
Z50 ∈ [ZFine Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200 ZSpline] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
1 ∈ [0 … 10] |
enableRelativeMove |
Enable the relative motion. Each waypoint define the joint displacement relative to the previous point. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
jntAccMultiplier |
The actual joint acceleration is equal to the reference joint acceleration multiplied by this parameter. The larger the value of this parameter, the larger the value of the actual joint acceleration. |
DOUBLE |
none |
1.0 ∈ [1.0 … 4.0] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Robot Joint Position Description
The complete description of a joint waypoint (JPOS) is: A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the positions of external axes. You can only set the robot joint positions if external axes do not exist. For example: {jnt_def_1}.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: {jnt_def_2}.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate if the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

MovePTP
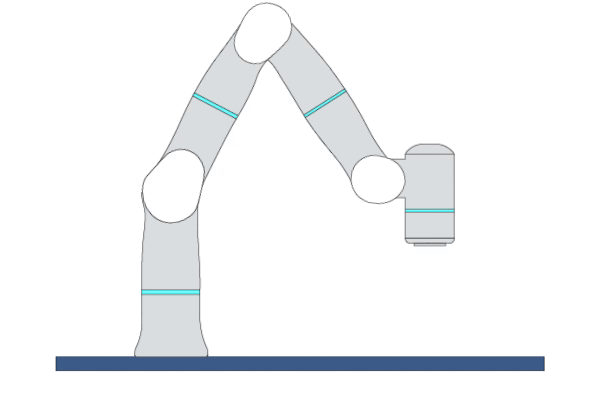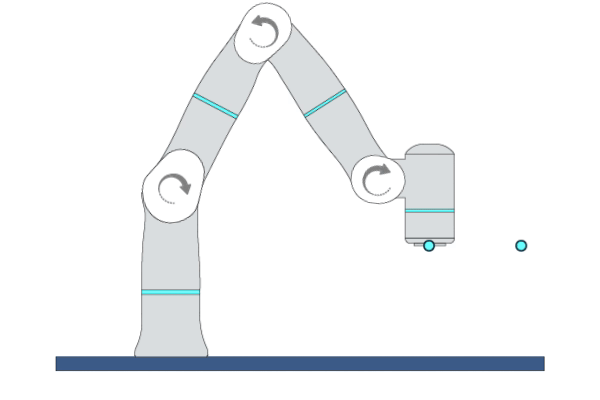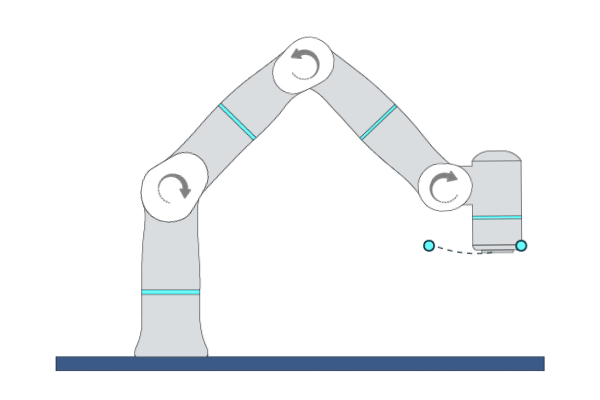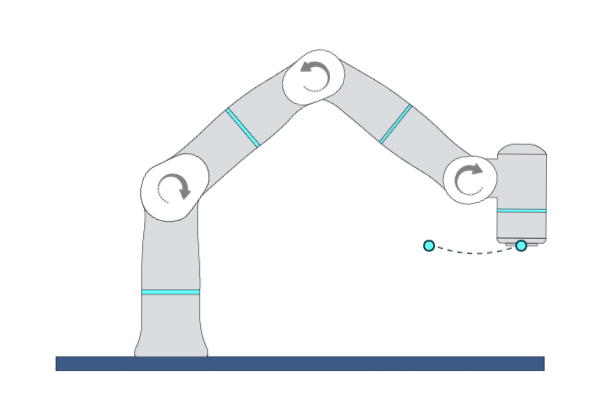
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: By calculating inverse kinematics, this primitive moves the robot TCP to the target pose by joint movement. You can specify multiple Cartesian waypoints before the target point, and the robot TCP will move in a non-linear way through each waypoint to reach the target point.
Example Usage: Use this primitive to quickly move the robot TCP to the specified positions in an obstacle-free space. Recommended for scenarios where the target point is Cartesian pose and the motion trajectory is not strictly required.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
waypoints |
Waypoints between initial and target poses |
ARRAY_COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
jntVelScale |
Robot joint velocity scale. The robot joints will move at full speed when this value is set to 100. |
INT |
none |
20 ∈ [1 … 100] |
zoneRadius |
Blending zone radius while TCP approximates the waypoints |
TYPE |
none |
Z50 ∈ [ZFine Z5 Z10 Z15 Z20 Z30 Z40 Z50 Z60 Z80 Z100 Z150 Z200 ZSpline] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
1 ∈ [0 … 10] |
enableFixRefJntPos |
Flag to indicate if fixed reference joint position is enabled. If this parameter is set to TRUE, the primitive will use the value of parameter [refJntPos] as the fixed joint reference position instead of the reference joint position of each waypoint during execution. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
refJntPos |
Reference target joint positions. When the robot moves in Cartesian space, each joint will move as close as possible toward the reference position. |
JPOS |
deg |
0.0 -40.0 0.0 90.0 0.0 40.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 |
jntAccMultiplier |
The actual joint acceleration is equal to the reference joint acceleration multiplied by this parameter. The larger the value of this parameter, the larger the value of the actual joint acceleration. |
DOUBLE |
none |
1.0 ∈ [1.0 … 4.0] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
*Robot Joint Position Description
The complete description of a joint waypoint (JPOS) is: A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the positions of external axes. You can only set the robot joint positions if external axes do not exist. For example: {jnt_def_1}.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: {jnt_def_2}.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate if the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |

MoveC
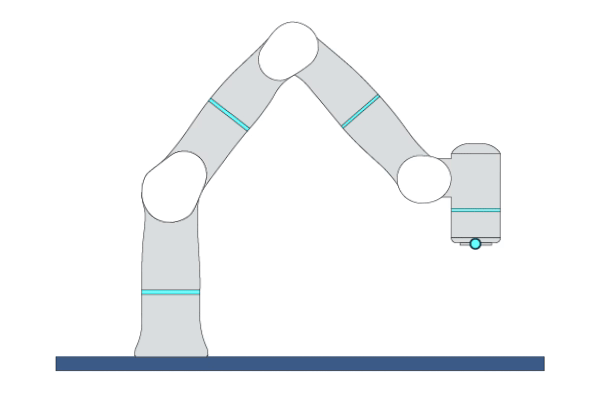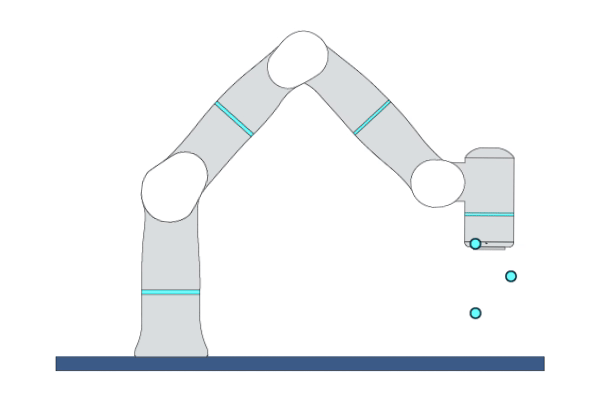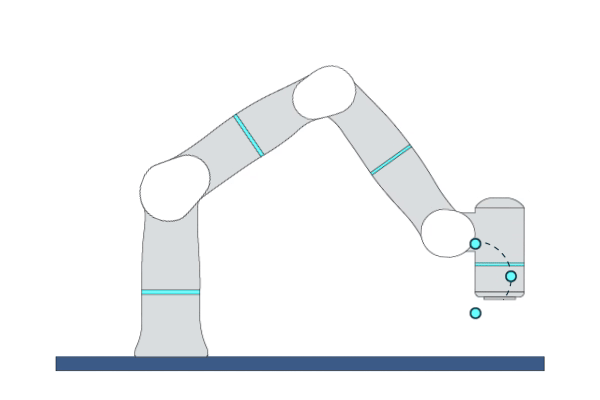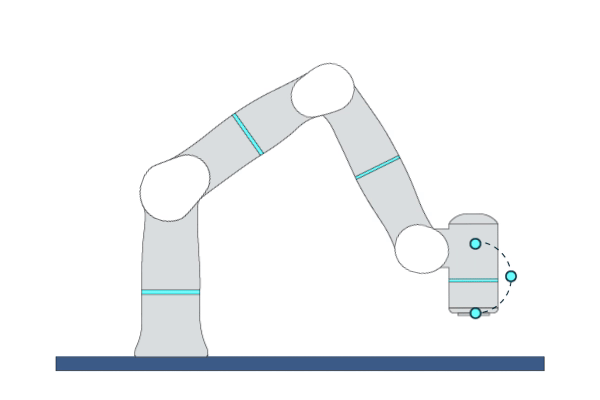
Primitive Description and Usage
Description: This primitive moves the robot circularly to a target pose in Cartesian space. The robot’s initial pose, middle pose, and target pose must not be collinear. A complete circle can be performed by two MoveC primitives.
Example Usage: Use this primitive in applications that require the robot to execute circular/arc trajectories.
Primitive Input Parameters
Input Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
Default Value & Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target* |
Target TCP pose |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* world*] |
middlePose* |
Middle pose of the circular arc. When passing through this point, the robot will refer to the reference joint position of the target point. |
COORD |
m-deg |
[traj_start* traj_goal* traj_prev* world*] |
vel |
TCP linear velocity |
DOUBLE |
m/s |
0.25 ∈ [0.01 … 2.0] |
targetTolerLevel |
Tolerance level to determine if the robot has reached the target. 1 means to check with the smallest tolerance, 0 means no tolerance check. |
INT |
none |
3 ∈ [0 … 10] |
acc |
TCP linear acceleration |
DOUBLE |
m/s^2 |
1.5 ∈ [0.1 … 3.0] |
angVel |
TCP angular velocity |
DOUBLE |
deg/s |
150.0 ∈ [10.0 … 500.0] |
enableFixRefJntPos |
Flag to indicate if fixed reference joint position is enabled. If this parameter is set to TRUE, the primitive will use the value of parameter [refJntPos] as the fixed joint reference position instead of the reference joint position of each waypoint during execution. |
BOOL |
none |
0 ∈ [0 / 1] |
refJntPos |
Reference target joint positions. When the robot moves in Cartesian space, each joint will move as close as possible toward the reference position. |
JPOS |
deg |
0.0 -40.0 0.0 90.0 0.0 40.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 |
jerk |
TCP linear jerk |
DOUBLE |
m/s^3 |
100.0 ∈ [90.0 … 10000.0] |
configOptObj |
Weights of three configuration optimization objectives during robot motion, which respectively are to make the robot easier to translate in Cartesian space, easier to rotate in Cartesian space, and closer to the reference joint position. |
VEC_3d |
none |
0.0 0.0 0.5 ∈ [0.0 0.0 0.1 … 1.0 1.0 1.0] |
*Parameters marked with an asterisk must be assigned a value prior to executing the primitive.
*Coordinate System Definition
Coordinate |
Definition |
Value Format |
|---|---|---|
world |
WORLD coordinate system, which is a fixed Cartesian coordinate system located at the center of the robot base |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN |
work |
WORK coordinate system, which defines the position of the workpiece relative to the WORLD coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz WORK WorkCoordName |
tcp |
TCP coordinate system, which is located at the Tool Center Point relative to the center of robot flange |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP ONLINE |
tcp_start |
The fixed coordinate system which is located at the initial TCP pose of the primitive |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TCP START |
traj_start |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the initial TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ START |
traj_goal |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the target TCP pose in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ GOAL |
traj_prev |
The offset of a waypoint relative to the previous waypoint in the TCP coordinate system |
X Y Z Rx Ry Rz TRAJ PREVIOUSWAYPOINT |
You can use the simplified value format above to describe a waypoint, while the complete description of a Cartesian waypoint is: X Y Z Rx Ry Rz ReferenceCoordinate A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the preferred joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the target positions of external axes. The additional data can be added if necessary.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: 0.2 0 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN : 0.2 0.1 0.3 0 180 0 WORLD WORLD_ORIGIN.
*Robot Joint Position Description
The complete description of a joint waypoint (JPOS) is: A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6. A1 to A7 are the joint positions of the robot; X1 to X6 are the positions of external axes. You can only set the robot joint positions if external axes do not exist. For example: {jnt_def_1}.
Add “:” to separate the waypoints. For example: {jnt_def_2}.
Primitive State Parameters
State Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
terminated |
The termination flag of the primitive. It is set to true if the primitive is terminated. |
BOOL |
none |
timePeriod |
The time spent on running the current primitive. |
DOUBLE |
s |
reachedTarget |
Flag to indicate if the robot has reached the target |
BOOL |
none |
waypointIndex |
Index of the current waypoint the robot just passed. 0 means the initial pose. |
INT |
none |
Primitive Output Parameters
Output Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
tcpPoseOut |
The TCP pose when the primitive is terminated. It is represented in the world coordinate system. |
COORD |
m-deg |
Default Transition Condition
State Parameter |
Condition |
Value |
|---|---|---|
reachedTarget |
= |
1 |
